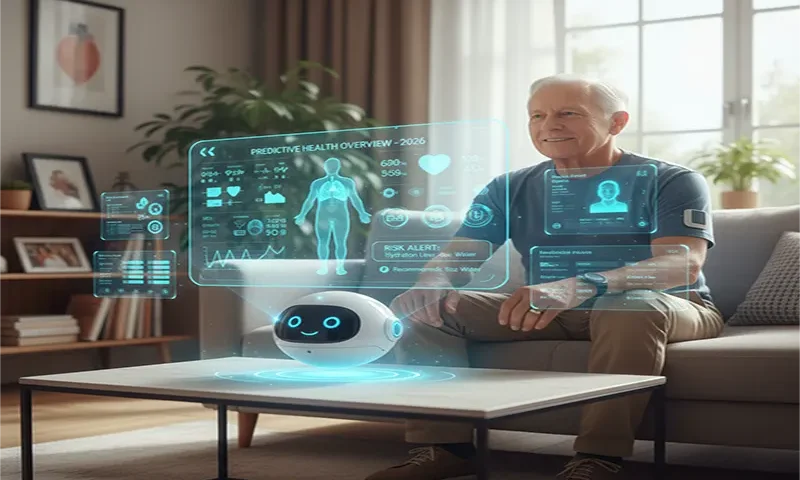
For decades, chronic disease management was a game of “catch-up.” A patient with heart failure would wait for overt symptoms—shortness of breath or swollen ankles—before seeking care, often resulting in an expensive emergency room visit. By 2026, the paradigm has shifted. The “Hospital-at-Home” model has matured from a pilot project into a global standard, powered by Multimodal AI Agents. These are not mere monitoring tools; they are autonomous digital guardians that fuse disparate data streams to predict clinical decline days before a patient even feels unwell.
Beyond Single-Stream Data: The Power of Sensor Fusion
In 2024, remote monitoring was often limited to single-parameter alerts—a “high heart rate” or “low oxygen” notification. In 2026, Multimodal AI leverages Sensor Fusion to create a high-definition picture of patient health. By correlating physiological, behavioral, and environmental data, these agents detect cross-parameter interactions that humans might miss.
Multimodal Data Fusion: From Modality to Clinical Insight
| Modality | Data Source | Clinical Insight (Predictive Value) |
| Physiological | Wearables (ECG, SpO2, HRV) | Detects autonomic nervous system stress and arrhythmias. |
| Acoustic | Ambient Mic (Voice/Cough) | Raspy voice or cough patterns can predict COPD flare-ups 72 hours early. |
| Ambient Sensing | WiFi-motion / LiDAR | Monitors gait speed and sleep cycles without wearable “friction.” |
| Environmental | Smart Home Sensors | Correlates high humidity or pollutants with respiratory triggers. |
| Behavioral | App usage / Meal photos | Identifies cognitive “slips” or dietary non-compliance in diabetics. |
Agentic Autonomy: Moving from Alerting to Acting
The “Agentic” shift in 2026 means these systems possess Reasoning and Planning capabilities. When an agent detects a Trend Divergence—for example, a heart failure patient whose “resting heart rate is rising” while their “ambient movement is decreasing”—it doesn’t just send a red flag to a busy nurse.
It utilizes Agentic Reasoning to:
- Validate: It asks the patient a targeted question via a voice interface: “I noticed you’ve been resting more today; are you feeling any extra fatigue?”
- Triage: Based on the voice analysis (detecting “breathiness”), it elevates the risk score.
- Execute: It autonomously schedules a telehealth “spot check” and sends a pre-visit summary to the physician, ensuring that intervention happens before the patient reaches a state of crisis.
The “Digital Twin” at Home
Central to this predictive power is the Personalized Digital Twin. By 2026, every high-risk chronic patient has a virtual counterpart that lives in the cloud (or on a secure edge server). This twin is fed by longitudinal data, allowing the AI to run “what-if” simulations.
If a diabetic patient’s glucose levels are trending high, the agent can simulate how a 10% increase in basal insulin or a 20-minute walk would impact their specific metabolism. This moves care from “one-size-fits-all” guidelines to a “One-size-fits-one” predictive protocol.
Invisible Sensing and the End of “Wearable Fatigue”
One of the biggest breakthroughs of 2026 is Ambient Sensing. Using low-power WiFi signals or LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), agents can monitor a patient’s breathing rate, heart rate, and even “fall risk” through walls, without the patient needing to wear a watch or chest strap. This “invisible” layer of protection is vital for elderly patients with dementia or those who suffer from wearable fatigue.
The Trust and Ethics Frontier: Privacy at the Edge
Continuous home monitoring raises valid concerns about “Surveillance vs. Care.” To solve this, 2026 has adopted Federated Learning as the privacy standard.
- Local Processing: Sensitive audio and motion data are processed on an “Edge AI” device (like a smart hub) inside the home.
- Global Learning: Only the “mathematical insights” (not the raw data) are sent to the cloud to help improve the AI for other patients.
This ensures that “what happens in the living room, stays in the living room,” while still allowing the medical agent to remain globally “smart.”
Economic Impact: The Trillion-Dollar Shift
The economic case for multimodal agents is undeniable. Early 2026 data shows that predictive at-home agents have reduced 30-day readmission rates by 15–20%. By catching exacerbations early, health systems are saving an average of $12,000 per avoided hospitalization. For insurers, this shift toward “Predictive Wellness” is transforming the payer model from a “sick-care” system to a “preventative-care” partnership.
The Primary Site of Clinical Intelligence
By the end of 2026, the hospital will no longer be the center of the healthcare universe—the home will be. Multimodal AI agents have become the “clinical glue” that holds a patient’s health journey together. By listening to the subtle whispers of a cough, watching the steady rhythm of a gait, and analyzing the pulse of a wearable, these agents ensure that for chronic patients, the future is no longer a series of emergencies, but a managed, predictable path toward longevity.